
More Resource: What is Metal and Their Types? Alkali Metals The metals consist of alkali metals, alkaline earth, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. They are grouped together in the middle to the left-hand side of the periodic table. Most elements on the periodic table are metals. In general, metal and nonmetals combine to form ionic compounds, while nonmetals combine with other nonmetals to form covalent compounds (molecules). Ionic bonds form when there is a transfer of electrons from one species to another, producing charged ions that attract each other very strongly by electrostatic interactions, and covalent bonds, which result when atoms share electrons to produce neutral molecules. When elements combine to form compounds, there are two major types of bonding that can result. The metals are to the left of the line (except for hydrogen, which is a nonmetal), the nonmetals are to the right of the line, and the elements immediately adjacent to the line are the metalloids. Many periodic tables along the right side of the table separate metals from nonmetals. These semiconductors are extremely important in computers and other electronic devices. In their physical properties, they are more similar to nonmetals, but under certain circumstances, some of them can be made to conduct electricity. The metalloids are intermediate in their properties.

Nonmetals are (usually) poor conductors of heat and electricity and are not malleable or ductile Many of the elementary nonmetals are gases at room temperature, others are liquids, and others are solids. Most metals are solids at room temperature with a characteristic silvery luster (with the exception of mercury, which is a liquid). Metalsare good conductors of heat and electricity, and are malleable (they can be swaged into sheets) and ductile (they can be drawn into wire).
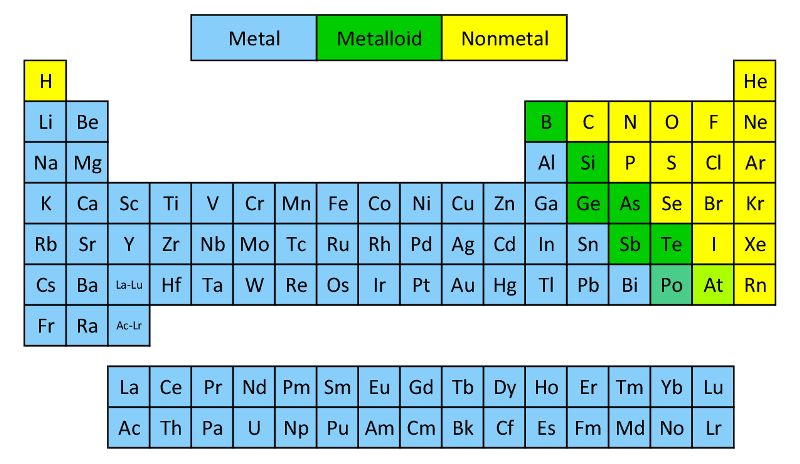
The elements can be classified as metals, nonmetals, or semimetals (metalloids).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
